Ceramic-to-metal brazing parts
(95%alumina ceramic and Kovar brazing part)
The realization of a reliable connection between ceramics and metal is the key to promoting the application of ceramic materials. The biggest difficulty in the connection process between ceramics and metal lies in the large difference between the coefficients of thermal expansion of ceramics and metal, which generates large residual stresses at the sealing interface after the connection is completed and reduces the joint strength, as well as the relatively poor wetting effect of metal on the surface of ceramics, which does not allow for the simple realization of the connection between ceramics and metal.
Materials | melting point (°C ) | modulus of elasticity(Gpa) | Coefficient of linear expansion(10-6)/(m.°C-1 ) |
Al2O3 | 2070 | 304~382 | 6.6-8.0 |
Si3N4 | 1880 | 320 | 3.0 |
SiC | 2970 | 420 | 4.3-4.8 |
TiC | 3160 | 460 | 7.4 |
Cu | 1084 | 110~128 | 17 |
Aluminum | 550~640 | 72 | ~20 |
Steel | 1400-1600 | 172~206 | 12~13.5 |
Ni | 1453 | ~200 | 8.5 |
(Properties of typical ceramics and metals)
At present, brazing is the most common method of joining ceramics to metals.
Brazing is a welding technique that uses a material with a lower melting point than the base material as the brazing material, and adopts a welding temperature slightly higher than the melting point of the brazing material to make the brazing material melt, wet the surface of the material to be connected, and then fill the gap of the joint, and realize the connection through the mutual diffusion of the elements between the base material and the brazing material.
For brazing ceramic to metals, the following two aspects require special attention:
- Improved wettability
The brazing material has a small wetting angle on the ceramic is a prerequisite for the realization of a metallurgical connection. Since the wettability between metal and ceramic is usually poor, or even non-wetting, to make the brazing material wet the surface of ceramic, the surface metallization of ceramic is often used or active metal elements (Ti, Zr, Hf, V) are added to the brazing material to improve the wettability between the brazing material and ceramic material.
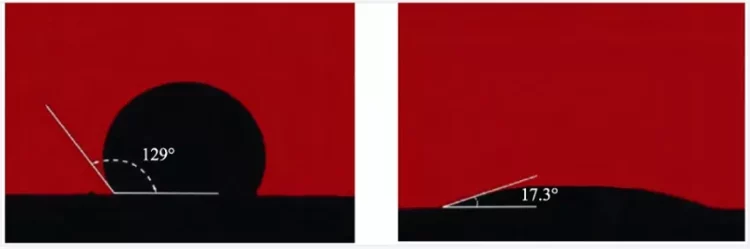
(AgCu VS AgCu-4.5Ti Infiltration angle)
(2) Reduce residual stress
Due to the large difference in expansion coefficient between metal and ceramic, it is easy to produce large residual stress in the joint, resulting in low joint strength. Therefore, when brazing ceramic materials and metals, special intermediate layers or composite brazing materials are often added to alleviate the residual stress, thus improving the strength of the joint.

Ceramic to metal brazing parts customization service is provided by InSealing. Please feel free to contact us for any inquiries.


Comments
Post a Comment